”It is like instructing via a straw,” winced an engineering professor who had simply spent 13 weeks interacting via the Net with a dozen graduate college students. The members of his class, like greater than 1,000,000 others worldwide who now take programs totally on-line, downloaded his lecture notes from the Net, communicated with one another and their teacher via e-mail, and took exams by responding to questions on pc screens at house or at work. Even within the absence of face-to-face interactions within the classroom, these college students discovered that the comfort of Net training made studying via a straw very candy.
Since earlier than the times of Socrates, instructing has largely concerned flesh-and-blood instructors lecturing to their college students—beneath a tree, in a colonnaded stoa, or in a brick-and-mortar schoolroom. Right this moment, although, due to widespread entry to the Web, on-line training is enabling professionals to study from afar, protecting tempo with technological and managerial adjustments regardless of their heavy schedules.
E-learning, particularly for engineers and executives in expertise industries, has emerged as one of many fastest-moving developments in larger training. Hundreds of technical and administration programs, together with diploma and certificates packages, are actually being provided by universities, for-profit skilled improvement facilities, and business coaching amenities worldwide. Among the many largest of those is the College of Maryland’s College Faculty in Adelphi, which boasts an on-line scholar physique of greater than 30 000.
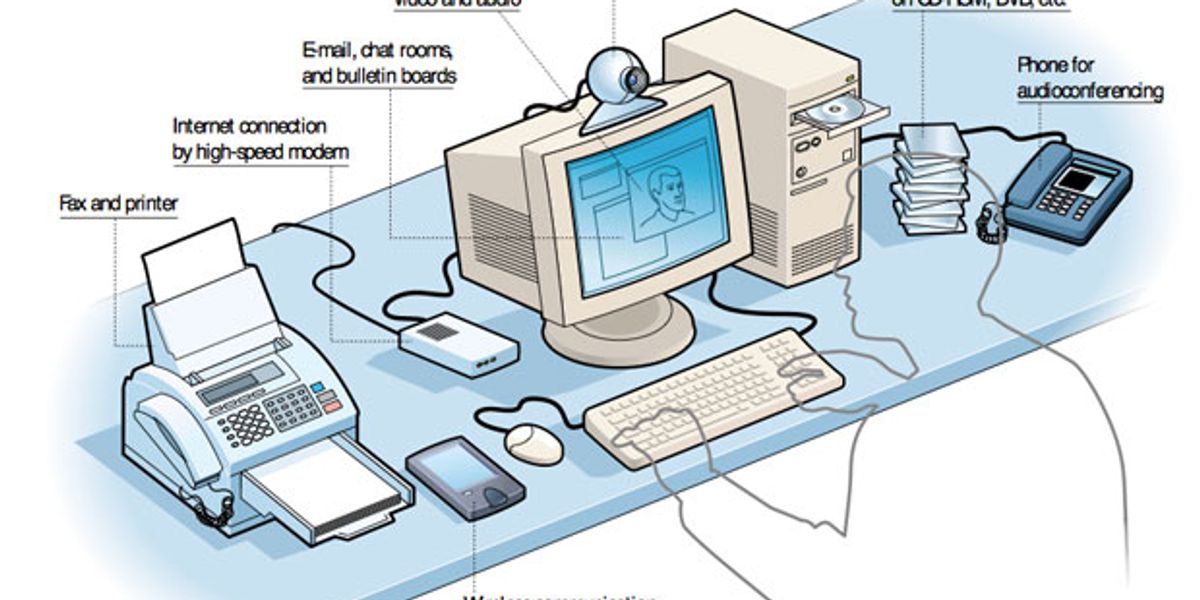
To make sure, the flexibility to instruct from afar is hardly new. As early because the mid-1800s, correspondence colleges in Europe have been instructing shorthand and international languages by mail. Within the final century, radio, tv, and satellite tv for pc broadcasting outfitted distance studying with new strategies of supply. The worldwide connectivity of the Web and a brand new technology of {hardware} and software program purposes underpin the instructing of programs over the Net [Fig. 1].
By nearly any measure, e-learning is booming. In line with a current U.S. authorities report, the demand for e-learning is prone to leap from simply 5 % of all college students in larger training in 1998 to 15 % by 2002. Within the company sector, spending on worker coaching final yr totaled $2.5 billion, about 40 % of which went to on-line training. What’s extra, business e-training is projected to double yearly over the subsequent a number of years. The educational on-line market can be anticipated to maneuver forward quickly, reaching practically $1.6 billion by 2002. What many educators are realizing is that e-learning is a development they will not ignore.
The engineer as e-learner
As any working engineer is aware of, there may be large stress to maintain tempo with the newest expertise and the most recent methods of doing enterprise. “Engineers inform me that they want an intensive refresher course of their specialties at the very least each different yr,” IEEE Spectrum was informed by Peter F. Drucker, the best-selling creator and administration guru. “And a ‘re-immersion’—their phrase—within the fundamentals at the very least each 4 years.”
But few engineers have the luxurious of attending lessons on well-groomed school campuses. Even those that do enroll in graduate college typically attend part-time within the evenings, speeding off to class after work, grabbing a chunk to eat alongside the way in which. When the bell rings on the finish of sophistication, they’re quickly again within the parking zone, rushing off for house. For these part-time learners—the lion’s share of as we speak’s graduate inhabitants—the precise classroom could be much more alienating than the digital one.
“Site visitors and parking are two of my largest hassles,” mentioned Dean C. Reonieri Jr., a software program developer at Lucent Applied sciences Inc. who has been taking graduate programs via the Net from Stevens Institute of Expertise, in Hoboken, N.J. “The perfect factor about taking an on-line course for me is comfort.”
Gautham Natarajan, who works in community planning at AT&T Corp. in New Jersey, agrees. He enrolled in two on-line telecommunications programs provided by Stevens Institute final spring, and located it “very versatile. I might entry the programs each time I wished—at house, at work, wherever there was a pc close by.” Natarajan estimates that he saved 45 minutes in commuting every method.
The enterprise world can be discovering on-line studying to be a boon for worker coaching, particularly as extra companies turn into international enterprises. One company coaching govt recalled that, not way back, his mission was to offer lessons for engineers in two or three websites in New Jersey. Today he’s liable for coaching workers in a number of international locations in Europe, Asia, Australia, and Latin America.
Some companies now function “company universities” on-line—two examples are Dell Studying, for staff at Dell Laptop Corp., Spherical Rock, Texas, and SunU, run by Solar Microsystems Inc., Palo Alto, Calif. Many of those company websites collaborate with educational establishments to both ship programs straight out of the college catalog or produce custom-made programs. For-profit Websites are additionally popping as much as fill the technical coaching area of interest, providing product-specific programs in such subjects as Linux, Microsoft Home windows NT and 2000, and Novell Netware.
The digital classroom
Simply as in typical school rooms, the day-to-day actions of on-line training differ broadly. Faculty and college e-courses are likely to observe the usual educational calendar, lasting from 12 to 15 weeks. The trainer signifies at first of the time period what’s required—whether or not and when college students will take midterm or last exams and submit downside units or last tasks—and the way the course will probably be performed.
Usually, every course has its personal homepage on the Net, the place the teacher posts class supplies, comparable to lecture notes, homework issues, studying assignments, and video clips of lectures or demonstrations. Pedagogically, the Net’s archival capacity is one among its nice benefits over the classroom. Particularly, it permits “asynchronous” studying: college students can entry the course Site each time and wherever handy—at house earlier than work, throughout lunch breaks on the workplace, or in the course of the night time. In some circumstances, although, college students might have to log in at designated instances for reside Webcasts of lectures or for chat classes with classmates. Some programs additionally stipulate that college students present up on campus for an preliminary assembly with the teacher and different college students.
With many e-learning programs, although, the category by no means meets in individual. As a substitute, they convey on-line—not simply at hand in homework, but in addition to ask questions, touch upon class subjects, and reply to feedback and questions from others. The trainer might even break the category up into teams, to work on crew tasks or stories. That fosters what educators name “collaborative studying,” an interactive fashion of problem-solving that in lots of circumstances improves college students’ understanding.
“With out some type of dialogue, distance studying is fairly nugatory,” noticed Howard R. Budin, head of the Middle for Expertise and College Change at Academics Faculty in New York Metropolis. Like many e-teachers, Budin weights college students’ grades by their diploma of participation in on-line discussions. For probably the most half, although, e-learners’ grades are nonetheless decided largely by how they do on exams and homework.
E-learning expertise
From the coed’s perspective, the mechanics of on-line studying are so simple as logging on to the Web. To run most e-learning software program, the coed will want a Pentium-class PC with the newest model of Home windows, or else a recent-issue Macintosh. The machine ought to have enough random entry reminiscence (32MB or extra) and a modem that operates at 56 kb/s or larger. Additionally important is an account with an Web service supplier (ISP) that features e-mail and entry to the World Broad Net.
College students usually submit homework and typically exams as e-mail attachments, so that they want e-mail software program that handles attachments and a present model of a word-processing program like Microsoft Phrase or WordPerfect. As for Net browsers, the newest model of Netscape Navigator or Microsoft Web Explorer is normally really helpful. Different packages which may be required embrace Adobe Acrobat Reader, Home windows Media Participant, and RealPlayer.
The market in on-line studying has matured to the purpose the place there may be now first rate software program for designing, instructing, and administering a Net-based course [see “Popular e-learning software packages,”]. These differ in each technical sophistication and supposed viewers. Fundamental options embrace a person interface for importing and downloading course materials; sending and receiving e-mail; and giving and grading of e-exams. Many platforms additionally accommodate threaded dialogue lists, chat rooms, bulletin boards, and file sharing. Some enable streaming video and audio—for lectures and the like—though downloading such information might pose an issue for these and not using a high-speed broadband connection to the Web. Some platforms let the teacher monitor what every scholar reads on-line for the category.
Usually, a corporation will use one e-learning platform for all its programs. Loading the software program onto a community server is not any more durable than introducing different software program. Stevens, as an example, makes use of WebCT operating on an Apache model 1.3.9 Net server. In company environments, firewalls might block unsecured Net site visitors from intruding into firm programs; in that case, the software program could be mounted on a local-area community or intranet, or on a server that resides outdoors the firewall.
Many instructors need assistance organising their programs. Accordingly, organizations are participating “tutorial designers,” whose job description lies someplace between technical assist and training. Earlier than a course goes on-line, they work with the teacher to create the construction for it. As soon as the course is beneath method, they assist add course materials to the server and discipline questions on utilizing the e-learning software program.
Importing course materials is just not sophisticated. Suppose the fabric was created in Phrase. First, one saves it as a hypertext markup language (HTML) file; the file is then uploaded to a chosen slot on the server, in keeping with directions for the e-learning software program. Non-text information, like streaming video and applets, are uploaded in the identical method, right into a file database, with every merchandise hyperlinked to a location the teacher designates—a lecture space in Week 1, say, or a file of readings.
No important distinction
Do college students study as effectively on-line as they do on campus? Sure, based on the scholarly literature up to now. In a broadly cited report summarizing the outcomes of such research, Thomas L. Russell, director emeritus of tutorial telecommunications at North Carolina State College, at Raleigh, wrote, “The excellent news is that these ‘no important distinction’ research present substantial proof that expertise doesn’t denigrate instruction.”
At Stevens, teacher Hosein Fallah examined that assertion by instructing his course on U.S. telecommunications coverage each conventionally and on the Net. To get rid of any bias, Fallah graded the mid-term exams with out realizing which of the lessons they got here from. Because the literature predicted, the grades in each lessons have been virtually the identical.
Naturally, not each scholar will discover on-line studying to his or her liking. For one factor, it could require extra self-discipline and maturity than typical training.
Nor do all instructors take to e-learning. A standard criticism was articulated within the current best-seller The Social Lifetime of Data (Harvard Enterprise College Press, 2000) by Xerox Corp. chief scientist John Seely Brown and College of California at Berkeley historian Paul Duguid. They argue that many colleges are speeding to compete with for-profit corporations by providing cheap “unplug and pay” programs. Whereas on-line studying might add some worth to an training, the authors state, they can not exchange life on an actual campus. By the expertise of attending class and assembly informally with friends and lecturers, college students achieve greater than mere data. They study “distinct methods of judging what’s attention-grabbing, legitimate, important.”
Then, too, there are logistical questions raised by on-line studying. For the school professor, a chief concern is how a lot further time will probably be consumed by producing and instructing a Net-based course. Most teachers really feel their days are already full sufficient, what with classroom instructing, analysis, conferences, and different duties. For them, probably the most troubling thought could also be that they must dedicate lengthy hours responding to e-mail from college students.
Some on-line instructors do discover that the full time can far exceed a standard course’s classroom classes and workplace hours. Loretta Donovan, head of the space studying program at Mercy Faculty, Dobbs Ferry, N.Y., estimated that she devotes about 20 to 30 minutes per week per on-line scholar. Donovan as soon as obtained 160 messages in two days from her college students. “I am excellent at scanning,” she informed Spectrum. That further time is value spending, Donovan mentioned, as a result of on-line programs provide a “a lot richer expertise” than typical classroom instruction.
And never all instructors discover Net instructing extra time-consuming. Hosein Fallah figures he works the identical quantity on his typical and on-line lessons, however the time “is distributed in another way. As a substitute of being tied to a concentrated interval of classroom instructing and workplace hours, you are on-line daily.” And, as a result of Fallah additionally dietary supplements his conventional programs with Net supplies, he mentioned, “I now get plenty of e-mail from my in-class college students, too.” That development is seen elsewhere in larger training. Starting this semester at Georgia Tech, for instance, all on-campus undergraduate programs in electrical and pc engineering will embrace some e-learning parts.
Certainly, e-learning’s most profound impact is on campus, claimed Edward Borbely, head of the Middle for Skilled Improvement on the College of Michigan’s Faculty of Engineering. Whereas engineering instruction has historically concerned “writing on the board,” with little interplay amongst college students, he mentioned, “now professors are utilizing Websites as classroom instruments.” As a result of the Net forces lecturers to rethink their programs, many come away saying that their on-campus fashion has improved, Borbely mentioned.
To wean instructors from their dependency on classroom lecturing, Stevens Institute launched Net School Colloquia. This program provides these new to on-line instruction an opportunity to display their digital accomplishments and focus on their uneasiness about digital pedagogy. New e-teachers additionally obtain intensive coaching in Net software program. To date, the outcomes have been fairly optimistic, with some beforehand reluctant professors rising as e-learning fanatics.
Footing the e-learning invoice
Whereas the introduction of e-learning might not require breaking floor for brand spanking new buildings, mounting an e-learning website is “definitely not free,” noticed Georgia Tech vice provost Joseph DiGregorio. “We’re continually scraping for funds to launch new packages.”
School compensation is probably the most important price. DiGregorio estimated {that a} third of Georgia Tech’s on-line studying price range goes to salaries. At Stevens, Net school obtain two charges, one for growing their e-course, one other for instructing it over the Web. Further administrative and technical workers are additionally wanted to run Net studying packages, which, in contrast to conventional school rooms, have to be stored up and operating across the clock.
Add to that the prices of coaching, software program licenses, e-commerce purposes, Net design instruments, repairs of pc and telecommunications infrastructure, and the invoice for venturing into digital house rapidly balloons. Some establishments which have launched main e-learning ventures, amongst them Pennsylvania State College’s World Campus and the State College of New York’s Studying Community, have spent many thousands and thousands of {dollars} on infrastructure and workers.
For the coed, tuitions for Net-based programs are corresponding to these for typical lessons. No matter effort and time the coed might save in avoiding the commute to campus have to be balanced in opposition to the price of pc {hardware} and software program and Web service to entry the course on-line.
Nonetheless unanswered at most faculties is the query of mental property. Who owns e-learning programs? The professors who designed them? The college? Each? Though some universities have adopted insurance policies that seem to settle the matter amicably, it’s rising elsewhere as one of the contentious battles on campus.
The e-learning catalog
Fairly most likely sure varieties of instruction won’t ever go totally on-line, like laboratory programs that require entry to costly, specialised gear. That mentioned, a large assortment of technical subjects could be taught via the Net [see “A sampling of on-line engineering courses offered by U.S. universities,”].
SOURCE: American Society for Engineering Schooling, Alfred P. Sloan Basis, and particular person Websites. Contains solely packages taught solely on-line.
Stanford College, in California, was one of many first colleges to offer instruction over the Net, and it now affords, via its Middle for Skilled Improvement, greater than 250 technical and administration programs to some 5000 working professionals. College students can earn grasp’s levels or take quick programs in various engineering fields.
This yr, Stevens launched six on-line graduate packages, recognized collectively as WebCampus.Stevens. (The college continues to supply distance-learning packages at company websites utilizing interactive video.) Lately, the college teamed up with the IEEE (Spectrum’s writer) to co-sponsor graduate-level programs aimed toward “engineers in business who want applications-oriented talent upgrades helpful for his or her jobs and careers,” defined Peter Wiesner, the IEEE’s director of constant training. Beneath the phrases of the partnership, IEEE members obtain 10 % discount in tuition. The IEEE is pursuing comparable preparations with the New Jersey Institute of Expertise, Tempo College, and U.S. Open College.
One of many extra rigorous e-learning graduate packages is the grasp of engineering in skilled apply (MEPP) on the College of Wisconsin—Madison. Beneath improvement for six years, it’s a part-time, two-year program designed for working engineers. College students have enrolled from Maine to California and Florida to Washington and from a number of of the nation’s prime corporations—Boeing, Normal Electrical, Motorola. Apart from per week of orientation on campus at first of every educational yr, all of the programs are delivered over the Net. Among the many program’s extra revolutionary choices is a course on “Creating and Sustaining the Digital Engineering Workplace.”
In line with MEPP director Wayne P. Pferdehirt, it’s vital to watch college students’ progress. On-line counselors assist candidates register and apply for monetary assist. If the college has not heard from a scholar in just a few days, the counselor will observe her or him down. Typically such a scholar’s silence seems to imply that she or he is touring on enterprise.
An academic smorgasbord
Within the coming years, technological advances, comparable to wi-fi networking, will undoubtedly assist make e-learning extra engaging. And as high-speed, broadband Web connections turn into the norm, extra real-time, interactive makes use of of the Net will seem in on-learning lessons. That in flip might improve the sense of neighborhood amongst geographically scattered learners.
Due to the way in which individuals work as we speak and due to new life-style developments, to not point out information exhibiting that full-time, on-campus training occupies a a lot slimmer slice of the academic terrain, many faculties and universities imagine that introducing alternate options to traditional instructing is a matter of their survival as instructional establishments. Not that conventional school rooms will go away totally. Extra seemingly, e-learning will take its place alongside a spread of choices—an academic smorgasbord—from which the coed will be capable to choose precisely the appropriate course on the proper time and place.
To Probe Additional
The American Society for Engineering Schooling’s Persevering with Schooling and Distance Studying Catalog is on the market on the Net at http://www.learnon.org. It lists roughly 3000 programs, giving college, course titles, and mode of supply, amongst different attributes. Different sources are Peterson’s Information to Distance Studying Applications and the Princeton Evaluate’s The Greatest Distance Studying Graduate Colleges.
For a complete information to distance studying listserves, software program, coaching, collaborative environments, and Net course improvement instruments, see the Net Based mostly Studying Useful resource Library, hosted by Robert H. Jackson, at http://www.outreach.utk.edu/weblearning.
Information on educational distance studying in the USA seem within the Nationwide Middle for Schooling Statistics report, “Distance Schooling at Postsecondary Schooling Establishments: 1997-98,” by Laurie Lewis, et al. (U.S. Division of Schooling, Workplace of Academic Analysis and Improvement, Washington, D.C., 1999). The report is on-line at http://nces.ed.gov/pubs2000/2000013.pdf.
Thomas L. Russell’s report “The No Vital Distinction Phenomenon” (North Carolina State College, 1999) concludes that college students carry out about the identical in on-line programs and conventional school rooms.
Publications that cowl distance training extensively embrace the Journal of Asynchronous Studying Networks, at http://www.aln.org/alnweb/journal/jaln.htm, and American Journal of Distance Schooling, http://www.ed.psu.edu/ACSDE/ajde/jour.asp. Different good sources are the Chronicle of Larger Schooling and the magazines Converge and Educause Quarterly.
Concerning the creator
Robert Ubell is director of Net-based distance studying at Stevens Institute of Expertise, in Hoboken, N.J., the place he oversaw the launch of the college’s on-line graduate program, WebCampus.Stevens.
Spectrum editor: Jean Kumagai
