Dysfunctional and handbook monetary reporting processes are anticipated to value U.S. companies $7.eight billion this 12 months, in keeping with a brand new report, on account of monetary planning and evaluation groups spending not less than two hours on handbook work every week, with annual firm budgets taking as much as six months to arrange.
The report, launched Thursday by the monetary planning and reporting software program firm DataRails, along with economists on the College of Baltimore, examined the financial impression of monetary reporting processes within the U.S. The researchers did an financial evaluation based mostly on composite revenues of greater than 839,000 U.S. firms of various sizes.
The report comes at a time when firms are coping with the rising prices of products and supplies thanks to produce chain constraints and excessive charges of inflation, and are additionally going through severe shortages of finance and accounting workers.
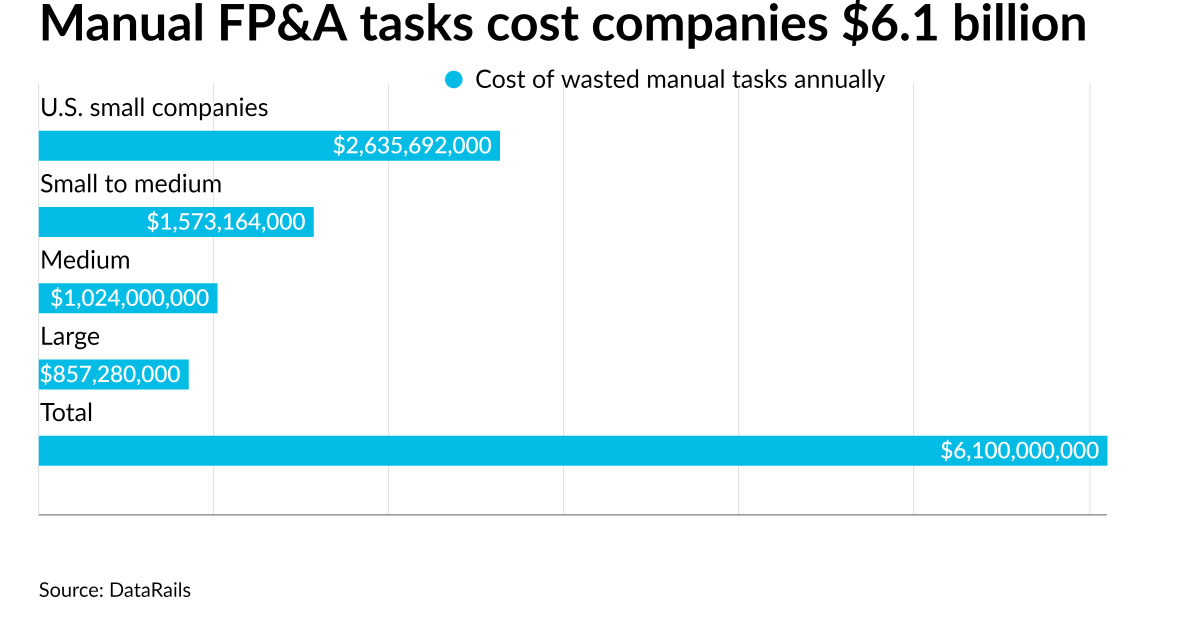
The report discovered that $6.1 billion of financial worth is misplaced every year because of inefficiencies within the conventional function of FP&A, making ready experiences reminiscent of P&L statements, steadiness statements and money flows utilizing handbook means, together with siloed methods of doing work and lack of knowledge integration. One other $1.7 billion is estimated to be wasted by failing to capitalize on progress alternatives in FP&A.
“Past the sizable $6.1 billion determine, the problem of handbook work additionally produces aspect financial downsides for companies,” mentioned the report, co-authored by College of Baltimore professors Roberto Cavazos and Mikhail Pevzner. “These symbolize oblique financial prices that harm the CFO workplace’s alternative to operate as a strategic advisor and create a bigger impression on the enterprise.”
The authors consider not less than one other $1.7 billion of alternative is failing to materialize because of a failure to push the correct levers and abilities throughout the FP&A operate.
The research analyzed the financial impression of handbook work regarding monetary reporting and the financial injury inflicting a drain in FP&A and general finance productiveness. It additionally examined longer-term financial worth and new sources of income that may be opened by means of the FP&A operate.
They pointed to the alternatives of utilizing extra automated FP&A methods, particularly within the face of the uncertainties attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic. With situation evaluation instruments, finance decision-makers will have the ability to establish ranges of potential outcomes and estimated impacts, consider the doable responses, and handle how the corporate will act given each optimistic and unfavourable prospects.
“Prior to now decade, FP&A has moved away from strict give attention to budgeting and P&Ls, steadiness sheets, and month-end reporting, towards changing into stewards of ‘worth creation,” mentioned the report. “This entails shifting past a standard reporting mindset to supporting top-line progress by means of well timed and related perception and foresight. This shift peaked throughout COVID-19 when bettering finance analytics, situation planning, and modeling capabilities, made the distinction between progress and failure for companies.”
